In gaming and high-performance computing, heat is the invisible enemy. One minute you're dominating a match—the next, your rig slows to a crawl, your screen stutters, and frustration takes over. Overheating doesn’t just hurt performance; it can crash your system entirely, turning epic gameplay into epic rage quits. That’s why cooling isn’t just a luxury—it’s mission-critical. Whether you're a seasoned PC builder or a casual gamer, keeping your system’s temperature in check is key to unlocking peak performance and long-term reliability. In this guide, we break down 10 smart, effective ways to cool your PC—from hardware upgrades to software adjustments. These aren’t just quick fixes—they’re long-term strategies designed to keep your machine cool under pressure. So before your next session turns into a meltdown (literally), let’s dive into the cooling tips every gamer and power user needs to know.
1. Understanding Thermal Dynamics in PCs

Before diving into cooling solutions, it's essential to grasp the basics of thermal dynamics in computers. Heat generation is a natural byproduct of electronic operations. CPUs and GPUs, being the most power-hungry components, generate the most heat. This heat can accumulate, raising the internal temperature and potentially damaging components if not managed properly. Understanding how heat moves within your PC case is crucial. Heat rises, so strategic placement of fans and vents can significantly impact cooling efficiency. Recognizing the role of thermal paste and heat sinks is also vital, as they facilitate heat transfer away from critical components.
2. Optimizing Airflow: The First Line of Defense

Proper airflow is the cornerstone of effective PC cooling. Ensuring a well-ventilated case with an appropriate number of intake and exhaust fans can drastically reduce internal temperatures. The goal is to create a consistent flow of air that moves heat away from components and out of the case. This involves choosing fans with the right size and speed, as well as positioning them to maximize airflow. Additionally, keeping dust filters clean and ensuring cables are neatly managed can prevent obstructions that impede airflow. An optimized airflow setup can significantly enhance cooling efficiency without additional hardware investments.
3. Liquid Cooling: A High-Performance Solution

For those seeking superior cooling performance, liquid cooling offers an advanced alternative. Unlike air cooling, liquid cooling systems use a liquid coolant to absorb and dissipate heat. These systems can be more efficient at maintaining lower temperatures, particularly under heavy loads. Liquid cooling setups often include a pump, radiator, and water blocks that directly contact the CPU and GPU. While more complex and expensive than air cooling, liquid cooling is ideal for overclocked systems or PCs used in demanding applications. It also has the added benefit of reducing noise levels, as fans can operate at lower speeds.
4. Thermal Paste: The Unsung Hero
The application of thermal paste is a critical yet often overlooked aspect of PC cooling. Thermal paste fills microscopic gaps between the CPU or GPU and the heat sink, ensuring efficient heat transfer. Over time, thermal paste can dry out, reducing its effectiveness. Regularly reapplying thermal paste, especially when upgrading or maintaining your PC, can prevent unnecessary thermal buildup. When choosing thermal paste, consider options with high thermal conductivity and low thermal resistance for optimal performance. Proper application technique is equally important, as too much or too little paste can impede heat transfer.
5. Undervolting: A Software-Based Approach

Undervolting is a technique that involves reducing the voltage supplied to your CPU or GPU, thereby decreasing power consumption and heat output. This method can be particularly effective for laptops or compact builds where space for additional cooling is limited. Undervolting requires careful adjustment, as reducing voltage too much can lead to instability. However, when done correctly, it can maintain performance while significantly lowering temperatures. Tools like Intel's XTU or AMD's Ryzen Master provide user-friendly interfaces for undervolting, allowing users to fine-tune their systems safely.
6. Case Selection: The Foundation of Cooling
Choosing the right case is fundamental to effective PC cooling. A case with good ventilation options, ample space for components, and support for additional cooling solutions is essential. Look for cases with multiple fan mounting points, support for liquid cooling radiators, and adequate clearance for large GPUs and CPU coolers. Some cases come with built-in features like fan controllers or noise-dampening materials, which can further enhance cooling performance. A well-designed case not only supports better airflow but also simplifies maintenance and upgrades, making it a long-term investment in your PC's health.
7. The Role of BIOS and Fan Curves

Adjusting fan curves in the BIOS can optimize cooling performance by controlling fan speeds based on temperature readings. Most motherboards allow users to customize fan curves, which dictate how aggressively fans respond to temperature changes. Setting a more aggressive fan curve can prevent temperatures from spiking during intensive tasks. Additionally, updating the BIOS can sometimes improve thermal management, as manufacturers release updates that enhance hardware compatibility and performance. Understanding how to navigate and adjust BIOS settings is a valuable skill for maintaining an efficient and cool-running PC.
8. External Cooling Solutions: Beyond the Case
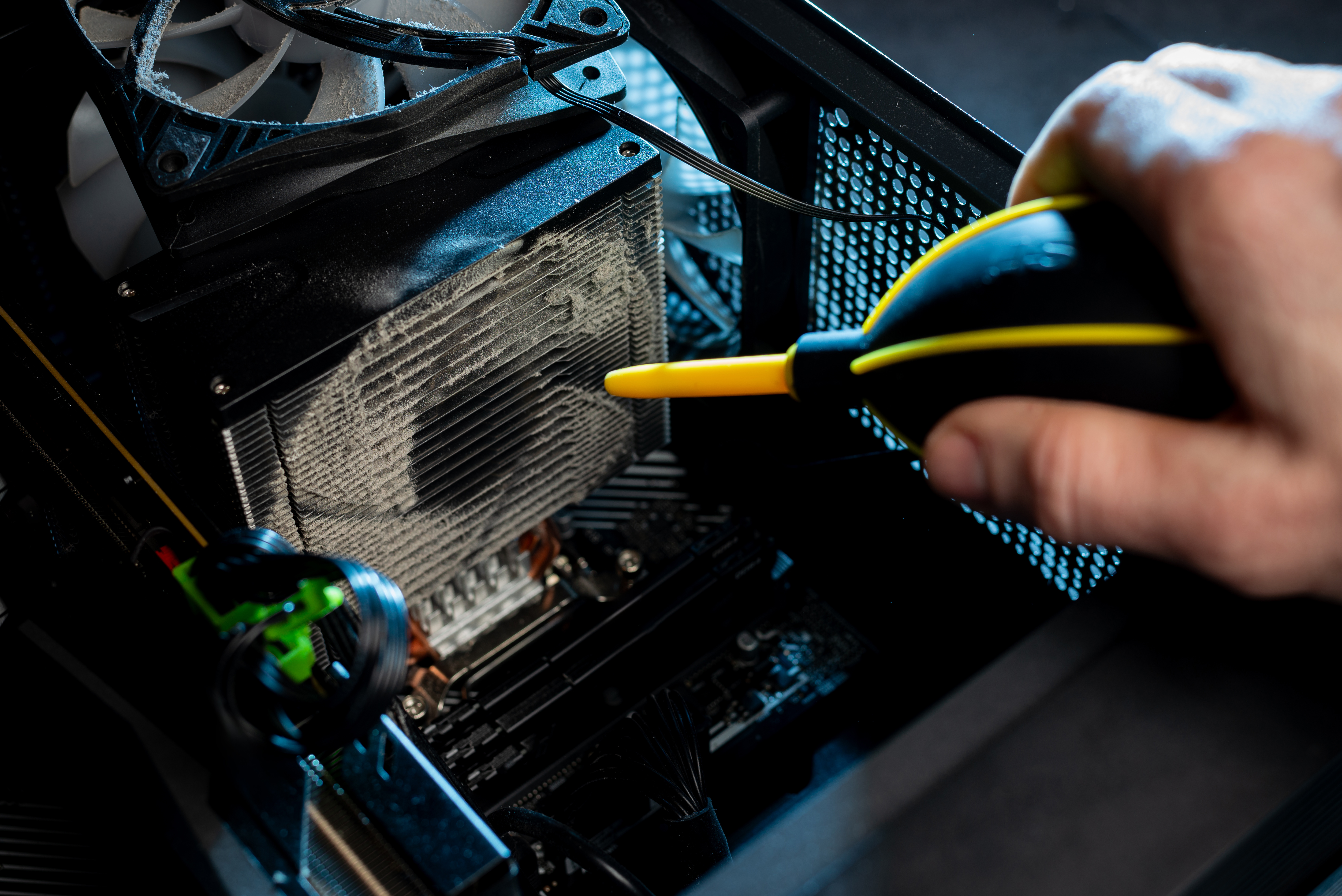

Sometimes, internal cooling solutions may not suffice, especially for high-performance builds. External cooling solutions, such as laptop cooling pads or desk fans, can provide additional airflow to keep temperatures in check. These solutions are particularly useful for laptops, which often have limited internal cooling capabilities. Cooling pads elevate the laptop, allowing air to circulate more freely, while desk fans can be positioned to direct cool air towards the PC. Although not a substitute for proper internal cooling, these external solutions can be effective supplementary measures.
9. Monitoring Tools: Keeping an Eye on Temperatures

Effective cooling management requires regular monitoring of temperatures and system performance. Software tools like HWMonitor, Core Temp, and MSI Afterburner provide real-time data on CPU, GPU, and overall system temperatures. These tools help identify potential thermal issues before they lead to throttling or hardware damage. By setting alerts for high temperatures, users can take proactive measures to adjust cooling settings or reduce workloads. Regular monitoring ensures that your cooling solutions are functioning as intended and provides peace of mind during intensive tasks.
10. Overclocking Considerations: Balancing Performance and Heat

Overclocking can significantly boost performance but also increases heat output. When pushing components beyond their factory settings, effective cooling becomes even more critical. Ensuring your cooling solutions are robust enough to handle the increased thermal load is paramount. This may involve upgrading to high-performance coolers or improving case airflow. It's also essential to monitor temperatures closely during overclocking to avoid overheating. Balancing the desire for higher performance with the need for stable, cool operation is a delicate art that requires careful planning and execution.
A Cool Path Forward
Navigating the complexities of PC cooling requires a blend of hardware knowledge and strategic planning. By understanding thermal dynamics and implementing a mix of cooling solutions, users can keep their systems running efficiently and avoid the pitfalls of thermal throttling. Whether through optimizing airflow, investing in liquid cooling, or employing software tweaks like undervolting, there are numerous ways to mitigate heat-related issues. By taking a proactive approach to cooling, you can ensure your PC remains a reliable and powerful tool, free from the frustrations of unexpected slowdowns or rage-inducing crashes.







